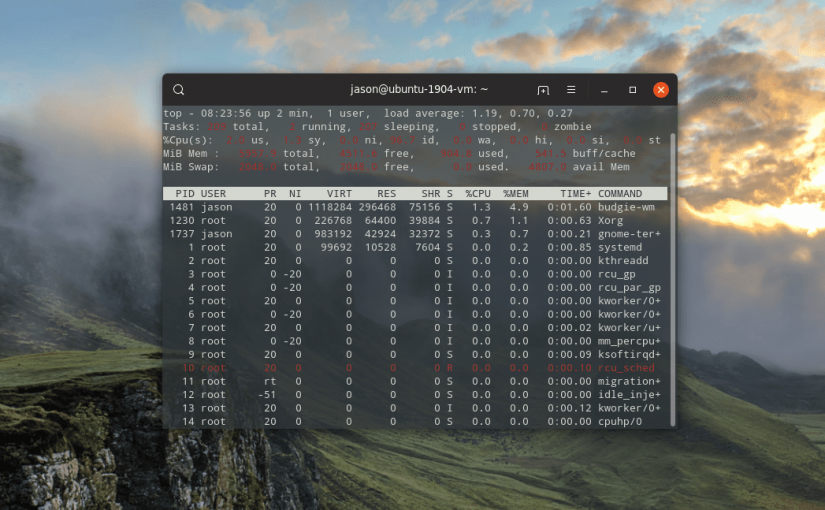
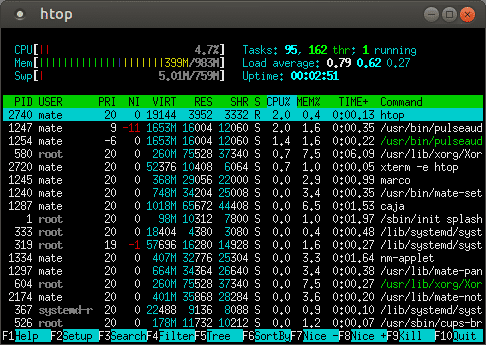
The Linux top command provides a terminal task manager which lists all of the running processes on the computer.
top
I use “Top” to kill a process within the top interface simply press k and enter the process id next to the application you wish to close. Top solicits a specific signal to send; in most cases, enter 15 (to request the process to gracefully terminate) or 9 (to immediately kill the process).
The first line offers some basic high-level info about the system:
- The time
- How long the computer has been running
- Number of users
- Load average
The load average shows the system load time for the last 1, 5 and 15 minutes.
The second line summarizes the number of ongoing, concurrent tasks:
- Total number of tasks
- Number of running tasks
- Number of sleeping tasks
- Number of stopped tasks
- Number of zombie tasks
The third line summarizes CPU performance:
- usage by the user
- usage by system
- usage by low priority processes
- usage by idle processes
- usage by io wait
- usage by hardware interrupts
- usage by software interrupts
- usage by steal time
The fourth line emphasizes memory:
- Total system memory
- Free memory
- Memory used
- Buffer cache
The fifth line highlights available swap space and total memory inclusive of swap:
- Total swap available
- Total swap free
- Total swap used
- Available memory
Main Table
The main table lists running processes:
- Process ID
- User
- Priority
- Nice level
- Virtual memory used by process
- Resident memory used by a process
- Shareable memory
- CPU used by process as a percentage
- Memory used by process as a percentage
- Time process has been running
- Command
Key Switches For the ‘top’ Command
Although you invoke top just by typing the name in a shell session, a few switches modify the utility’s behavior:
- -h: Show the current version
- -c: This toggles the command column between showing command and program name
- -d: Specify the delay time between refreshing the screen
- -o: Sorts by the named field
- -p: Only show processes with specified process IDs
- -u: Show only processes by the specified user
- -i: Do not show idle tasks




 MATE Terminal is a terminal emulation application that you can use to access a UNIX shell in the MATE environment. With it, you can run any application that is designed to run on VT102, VT220, and xterm terminals. MATE Terminal also has the ability to use multiple terminals in a single window (tabs) and supports management of different configurations (profiles). MATE Terminal is a fork of GNOME Terminal.
MATE Terminal is a terminal emulation application that you can use to access a UNIX shell in the MATE environment. With it, you can run any application that is designed to run on VT102, VT220, and xterm terminals. MATE Terminal also has the ability to use multiple terminals in a single window (tabs) and supports management of different configurations (profiles). MATE Terminal is a fork of GNOME Terminal.